Heart Illness Classification AutoEncoders
In this project, you will work with LSTM-based autoencoders to classify human heart beats for heart disease diagnosis. The dataset contains 5,000 Time Series examples with 140 timesteps. Each time-series is an ECG or EKG signal that corresponds to a single heartbeat from a single patient with congestive heart failure. An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a test that checks how your heart is functioning by measuring the electrical activity of the heart. With each heartbeat, an electrical impulse (or wave) travels through your heart. This wave causes the muscle to squeeze and pump blood from the heart. There are 5 types of hearbeats (classes) that can be classified: i) Normal (N); ii) R-on-T Premature Ventricular Contraction (R-on-T PVC); iii) Premature Ventricular Contraction (PVC); iv) Supra-ventricular Premature or Ectopic Beat (SP or EB); v) Unclassified Beat (UB). The shape of the time-series and the position of the impulses allows doctors to diagnose these different conditions. For the purposes of this project, we are interested in 2 classes: Normal and Abnormal (which includes class 2-5 above merged).
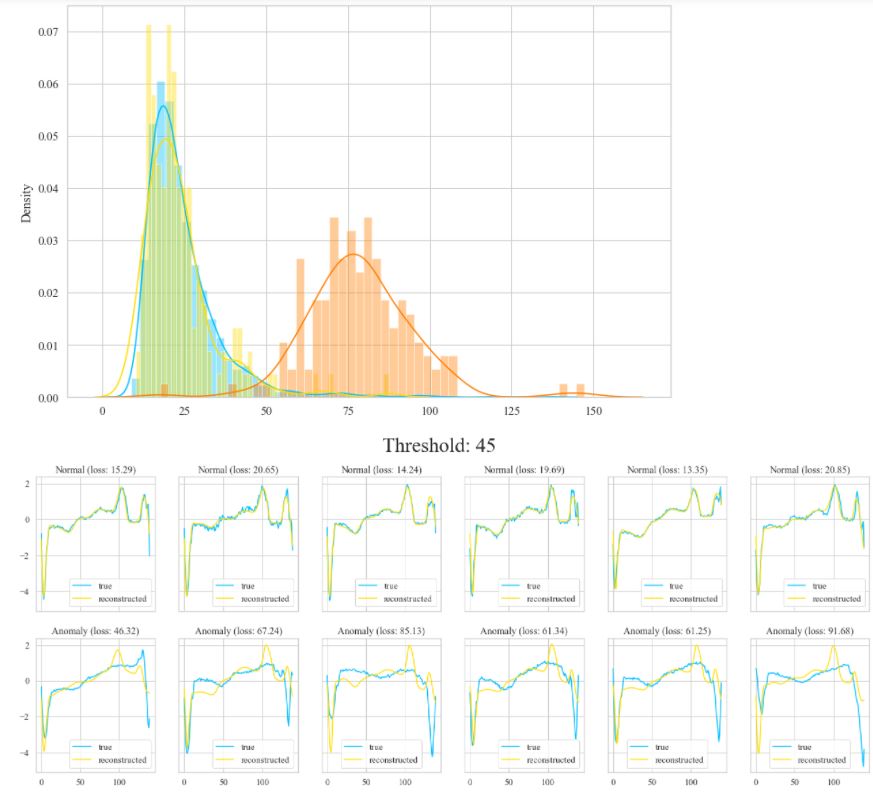
This is an example of an anomaly detection problem where class imbalance exists, i.e., number of each of the individual positive (abnormal) instances are smaller than the normal case. The autoencoder approach is suited well for such applications of anomaly detection. In anomaly detection, we learn the pattern of a normal process. Anything that does not follow this pattern is classified as an anomaly. For a binary classification of rare events, we can use a similar approach using autoencoders.